
E-Invoicing Under GST: Part 6 – E-Invoicing Workflow from Supplier to Invoice Registration Portal
Latest update: The government introduced a new GST e-invoice scheme under which businesses with turnover of Rs 500 crore and above will generate all invoices on a centralised government portal starting October 1, 2020. Earlier, the turnover threshold for businesses was set at Rs 100 crore.
There are a lot of questions around the flow of activities involved when you integrate e-invoicing into your business. To help you understand how to get started with e-invoicing, this article outlines the flow of activities between a supplier and the invoice registration portal.
Flow from Supplier (Seller) to Invoice Registration Portal (IRP)
Step 1
Once the invoice is generated by the seller using their own accounting or billing system, it needs to be uploaded to the invoice registration portal. The invoice can be generated using any software utility including those using Microsoft Excel or the Offline Utility provided by the GSTN. The invoice must conform to the e-invoice schema that is published and adheres to the mandatory parameters. The optional fields can be filled according to the business needs of the supplier. The supplier’s (seller’s) software should be capable of generating a JSON of the final invoice that is ready to be uploaded to the IRP. The IRP will only take JSON of the e-invoice.
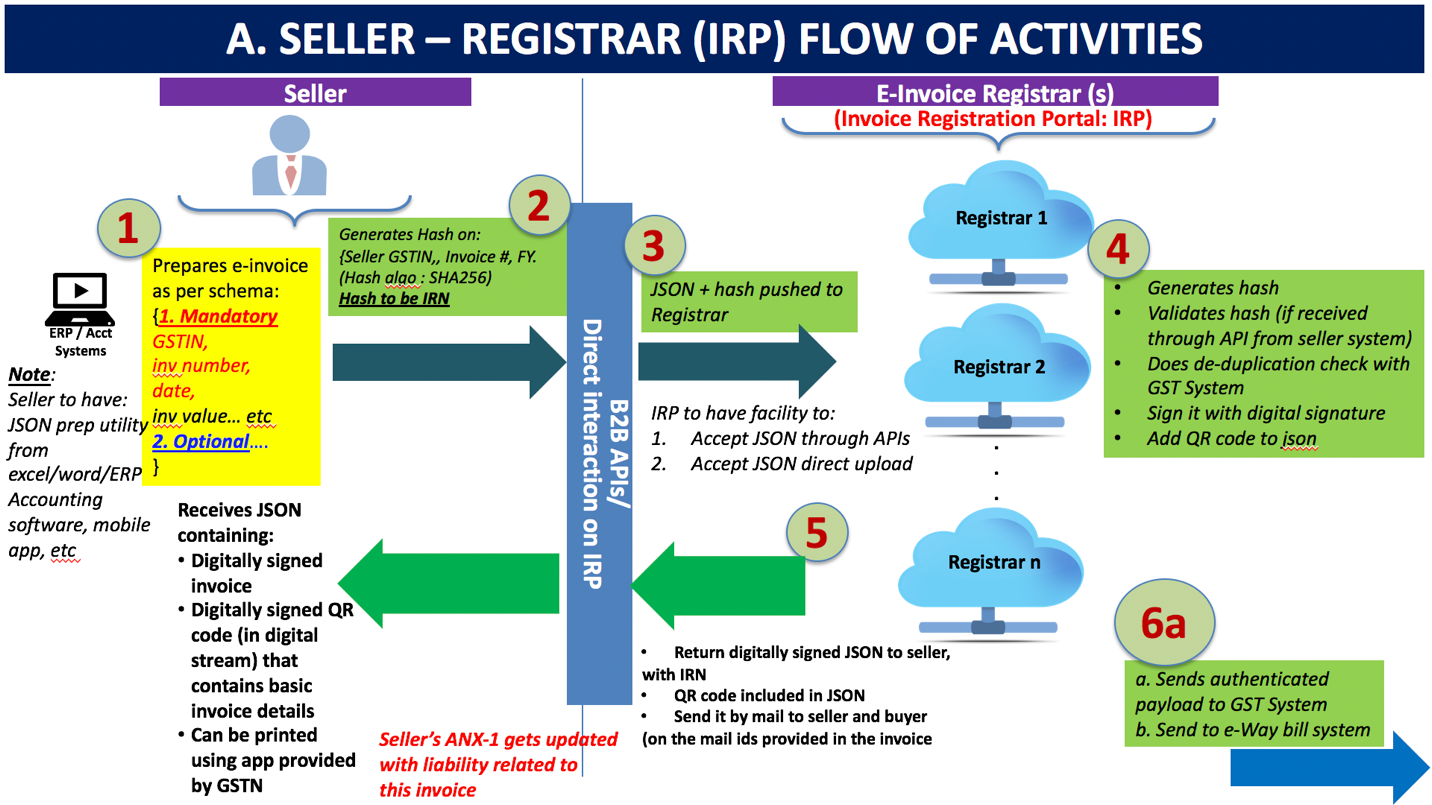
Note: Sellers should have a utility that will output invoice data in JSON format, either from their accounting or billing software or their ERP or excel/word document or even a mobile app. Those who do not use any accounting software or IT tool to generate the invoice, will be provided an offline tool to key-in data of invoice and then submit the same. Small and medium sized taxpayers (having annual turnover below Rs 1.5 Crores) can avail accounting and billing system being offered by GSTN free of cost.
Step 2
Once the invoice is uploaded to the Invoice Registration Portal, the system will generate a unique Invoice Reference Number (IRN) (in technical terms, it will be a hash of 3 parameters using a standard and well known hash generation algorithm e.g. SHA256). This is an optional step. The seller/supplier can also generate this hash and upload the same along with invoice data.
The 3 parameters which will be used to generate an IRN (hash) are:
- Supplier GSTIN
- Supplier’s invoice number
- Financial year (YYYY-YY)
(The IRN or hash generation algorithm will be prescribed by GSTN in the e-invoice standard).
Step 3
The seller is required to upload the JSON of the e-invoice (along with the hash, if generated) into the IRP. The JSON may be uploaded directly on the IRP or through GSPs or through third party provided Apps.
Step 4
The IRP will validate the hash of the uploaded JSON, if uploaded by the supplier. The IRP will check the hash from the Central Registry of GST System to ensure that the same invoice from the same supplier pertaining to the same Financial Year is not being uploaded again. On receipt of confirmation from Central Registry, IRP will add its signature on the Invoice Data as well as a QR code to JSON. The QR code will contain GSTIN of seller and buyer, Invoice number, invoice date, number of line items, HSN of major commodity contained in the invoice as per value, hash etc. The hash computed by IRP will become the IRN (Invoice Reference Number) of the e-invoice.
This shall be unique to each invoice and hence be the unique identity for each invoice for the entire financial year in the entire GST System for a taxpayer. [GST Systems will create a central registry where hash sent by all IRPs will be kept to ensure uniqueness of the same].
Step 5
One of the most significant benefits of integrating the e-invoicing system into your business operations is sharing the uploaded data with the GST and e-way bill system - this means no more multiple data entry.
Step 6
Finally, the system will return a digitally signed JSON with a unique Invoice reference number to the seller and a QR code. The registered invoice will also be sent to the seller and buyer on their email address as provided in the invoice - this will allow the buyer to accept or reject the invoice in real time, thereby saving time and avoiding instances of tax reconciliation.
To know more about our E-invoicing and GST compliance solutions, contact us here.
Follow our E-invoicing under GST Series on the links below:
- E-Invoicing Under GST: Part 1 - What is an e-invoice?
- E-Invoicing Under GST: Part 2 - E-invoicing and the Tax Department
- E-Invoicing Under GST: Part 3 - Benefits of e-invoicing
- E-Invoicing Under GST: Part 4 - Documents to be reported under e-invoicing
- E-Invoicing Under GST: Part 5 - How does e-invoicing work?
- E-Invoicing Under GST: Part 6 – E-Invoicing Workflow from Supplier to Invoice Registration Portal
- E-Invoicing Under GST: Part 7 - Workflow from IRP to Buyer and GSTN or E-Way Bill System
- E-Invoicing Under GST: Part 8 - Everything you need to know about Invoice Registration Portal
- E-Invoicing Under GST: Part 9 – Features of e-invoice system you need to know
- E-Invoicing Under GST: Part 10 – How to register your e-invoice
- E-Invoicing Under GST: Part 11 - Myths around e-invoicing
- E-Invoicing Under GST: Part 12 – Frequently asked questions on e-invoicing
Prepare your business for e-invoicing under GST
Discover how to meet all compliance requirements while integrating e-invoicing into your tax function.

Stay up to date
Sign up for our free newsletter and stay up to date with the latest tax news.



